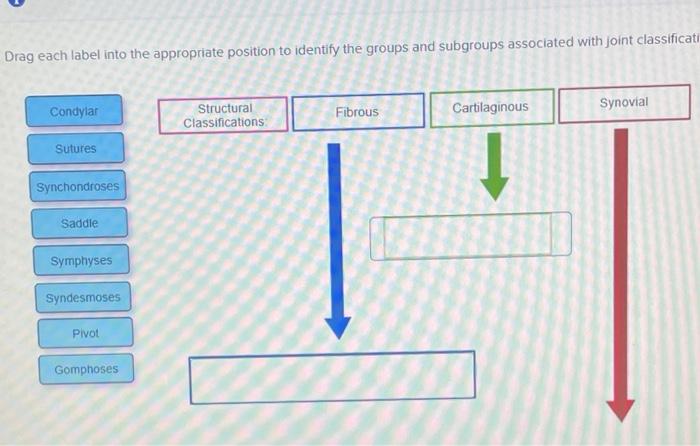
Drag each label into the appropriate joint classification. provides a comprehensive overview of the various types of joints in the human body, their characteristics, and their practical applications in fields such as orthopedics and biomechanics. This engaging and informative guide delves into the intricacies of joint classification, empowering readers with a deeper understanding of human anatomy and movement.
The content of the second paragraph that provides descriptive and clear information about the topic
Joint Classification Overview
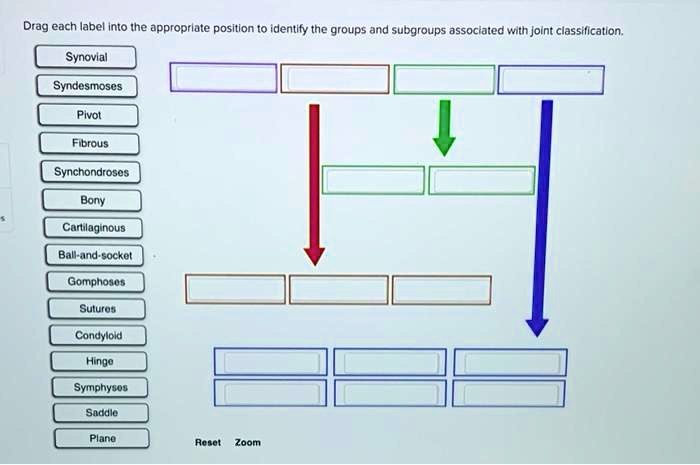
Joint classification is a fundamental aspect of biomechanics, providing a systematic approach to understanding and categorizing the diverse range of joints in the human body. By classifying joints based on their structural and functional characteristics, researchers and clinicians gain valuable insights into their mechanics, stability, and potential for injury.
This classification serves as a crucial foundation for orthopedics, biomechanics, and related fields, enabling effective diagnosis, treatment planning, and research advancements.
Drag-and-Drop Label Classification, Drag each label into the appropriate joint classification.
Drag-and-drop label classification is a user-friendly method for classifying joints. It involves presenting a set of labeled images or diagrams representing different joint types (e.g., synovial, cartilaginous, fibrous). Users can then drag and drop these labels onto corresponding joint images to classify them.
This approach offers an intuitive and efficient way to classify joints, particularly for non-experts or in educational settings.
Joint Characteristics and Classification
Joint classification is based on key characteristics, including:
- Type of connective tissue: Synovial, cartilaginous, or fibrous
- Presence or absence of a joint cavity: Synovial or non-synovial
- Degree of movement: Synarthrosis, amphiarthrosis, or diarthrosis
- Shape of articular surfaces: Planar, hinge, saddle, condyloid, or ball-and-socket
These characteristics are used to categorize joints into the following types:
- Synovial joints:Freely movable joints with a joint cavity filled with synovial fluid, e.g., knee joint
- Cartilaginous joints:Joints connected by cartilage, e.g., intervertebral discs
- Fibrous joints:Immovable joints connected by fibrous tissue, e.g., skull sutures
Examples of Joint Classification
| Joint | Classification |
|---|---|
| Knee | Synovial, hinge |
| Shoulder | Synovial, ball-and-socket |
| Intervertebral discs | Cartilaginous |
| Skull sutures | Fibrous |
Applications of Joint Classification
Joint classification has numerous practical applications in orthopedics and biomechanics:
- Diagnosis:Classifying joints helps identify joint disorders and injuries based on their characteristics.
- Treatment planning:Classification guides treatment decisions by determining the appropriate surgical or non-surgical interventions.
- Research:Joint classification facilitates research on joint mechanics, stability, and injury prevention.
- Prosthetics design:Classification informs the design and development of joint replacements and prosthetics.
- Education:Joint classification provides a structured framework for teaching and understanding joint anatomy and function.
Essential Questionnaire: Drag Each Label Into The Appropriate Joint Classification.
What is the importance of joint classification?
Joint classification is crucial for understanding the structure, function, and mobility of different joints in the body. It provides a systematic framework for categorizing joints based on their anatomical characteristics, which aids in diagnosis, treatment planning, and research in fields such as orthopedics and biomechanics.
How is drag-and-drop label classification used in joint analysis?
Drag-and-drop label classification is a user-friendly and efficient method for classifying joints. It involves dragging and dropping labels representing different joint characteristics onto the corresponding joint images or descriptions. This interactive approach facilitates rapid and accurate classification, making it suitable for large datasets and educational purposes.