Advanced hardware lab 7-5 identify network technologies – Embark on an enlightening journey with Advanced Hardware Lab 7-5: Identify Network Technologies, where we delve into the intricate world of network technologies, unraveling their complexities with precision and clarity. Our exploration will illuminate the diverse types of networks, their topologies, protocols, and security measures, empowering you with a comprehensive understanding of this foundational aspect of modern computing.
Overview of Network Technologies: Advanced Hardware Lab 7-5 Identify Network Technologies
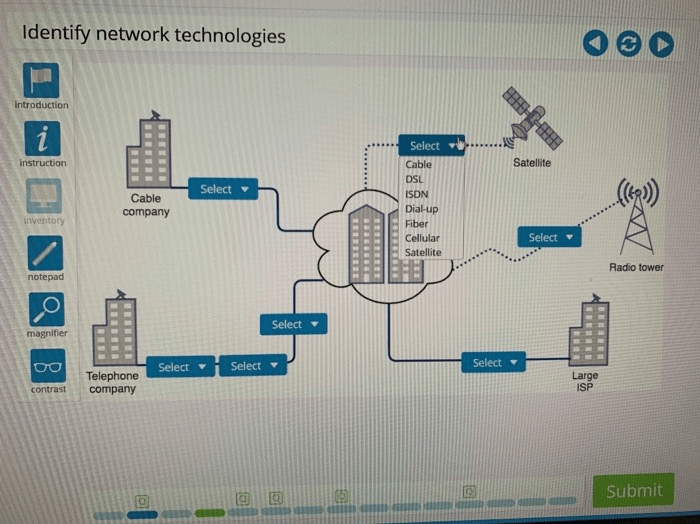
Network technologies are the foundation of modern communication and data exchange. They enable the interconnection of devices, allowing for the sharing of information and resources. Network technologies encompass both wired and wireless solutions, each with its own advantages and disadvantages.
Wired Network Technologies, Advanced hardware lab 7-5 identify network technologies
- Ethernet:A widely used wired technology that utilizes copper cables or fiber optics to transmit data at high speeds.
- Coaxial cable:An older technology that uses a single copper wire surrounded by insulation to transmit data.
- Fiber optic cable:A high-bandwidth technology that uses glass or plastic fibers to transmit data using light signals.
Wireless Network Technologies
- Wi-Fi:A wireless technology that uses radio waves to connect devices within a limited range.
- Bluetooth:A short-range wireless technology designed for connecting devices such as mobile phones, speakers, and keyboards.
- Cellular networks:A wireless technology that uses radio towers to provide mobile devices with internet access.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Wired and Wireless Technologies
- Wired technologies:Provide higher bandwidth and stability, but are less flexible and portable.
- Wireless technologies:Offer greater flexibility and mobility, but may experience interference and have lower bandwidth.
Network Topologies
Network topology refers to the physical arrangement of devices within a network. Different topologies have varying levels of connectivity, fault tolerance, and performance.
Types of Network Topologies
- Bus topology:A simple topology where all devices are connected to a single cable.
- Star topology:A topology where all devices are connected to a central hub or switch.
- Ring topology:A topology where devices are connected in a circular fashion, with data flowing in one direction.
- Mesh topology:A topology where each device is connected to multiple other devices, creating a redundant network.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Network Topologies
- Bus topology:Easy to implement and cost-effective, but can be prone to failures.
- Star topology:Provides better fault tolerance and scalability, but can be more expensive.
- Ring topology:Offers high reliability and bandwidth, but can be difficult to manage.
- Mesh topology:Provides excellent fault tolerance and scalability, but is complex and expensive to implement.
Network Protocols
Network protocols are sets of rules and procedures that govern the communication between devices on a network. They define how data is formatted, transmitted, and received.
Types of Network Protocols
- TCP/IP:A suite of protocols that provides reliable and secure communication over the internet.
- UDP:A protocol that provides unreliable but faster communication, suitable for applications such as video streaming.
- HTTP:A protocol used for transferring web pages and other data over the internet.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Network Protocols
- TCP/IP:Provides reliable and secure communication, but can be slower than UDP.
- UDP:Offers faster communication, but is unreliable and not suitable for applications that require data integrity.
- HTTP:Enables efficient transfer of web content, but is not secure by default.
Network Security
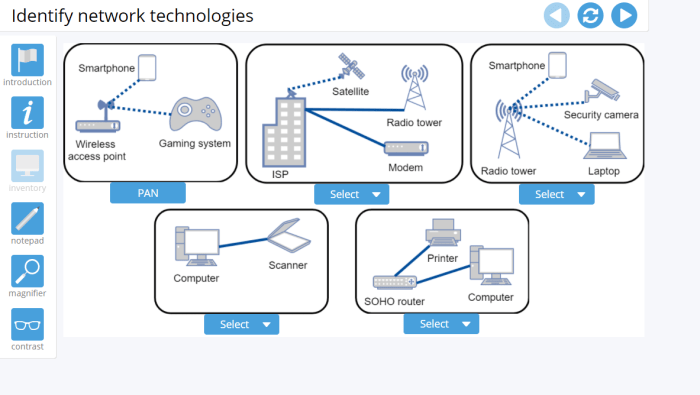
Network security involves protecting networks and data from unauthorized access, use, disclosure, disruption, modification, or destruction.
Types of Network Security Threats
- Viruses:Malicious software that can infect and damage computer systems.
- Malware:A general term for malicious software, including viruses, spyware, and ransomware.
- Hackers:Individuals who attempt to gain unauthorized access to networks or systems.
Types of Network Security Measures
- Firewalls:Hardware or software that blocks unauthorized access to networks.
- Intrusion detection systems (IDS):Monitor networks for suspicious activity and alert administrators.
- Encryption:A technique used to protect data from unauthorized access.
Network Troubleshooting
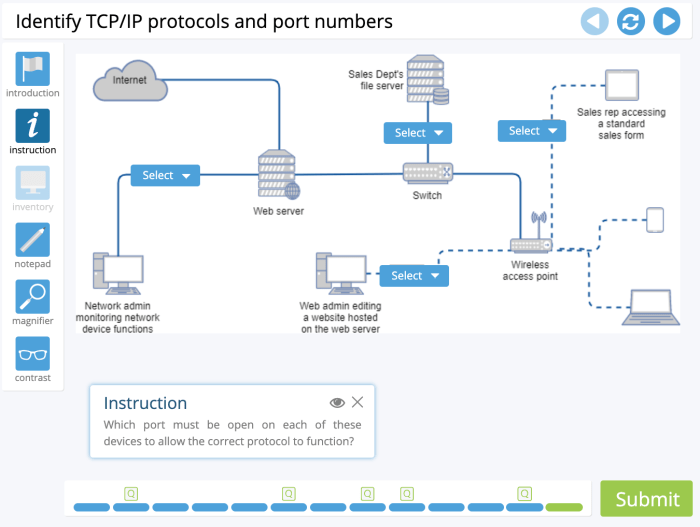
Network troubleshooting involves identifying and resolving problems that affect network performance or connectivity.
Steps in Network Troubleshooting
- Identify the problem:Determine the symptoms and impact of the network issue.
- Gather information:Collect data on network devices, configurations, and logs.
- Test and isolate the problem:Perform tests to pinpoint the source of the issue.
- Resolve the problem:Implement corrective actions to fix the issue.
- Verify the solution:Ensure that the network issue has been resolved and that the network is functioning properly.
Common Network Problems
- Connectivity issues:Devices cannot connect to the network or access the internet.
- Performance issues:Slow network speeds or unreliable connections.
- Security breaches:Unauthorized access or data theft.
Tools and Techniques for Network Troubleshooting
- Ping:A utility used to test network connectivity and latency.
- Traceroute:A tool that displays the path taken by data packets through a network.
- Network analyzers:Software or hardware tools that capture and analyze network traffic.
Popular Questions
What is the difference between a bus and a star network topology?
In a bus topology, all devices are connected to a single shared cable, while in a star topology, each device is connected to a central hub or switch.
What is the role of TCP/IP in network communication?
TCP/IP is a suite of protocols that enables communication between devices on a network by providing a common set of rules and procedures.
How does a firewall protect a network from security threats?
A firewall monitors and controls incoming and outgoing network traffic, blocking unauthorized access and preventing malicious activity.