Traumatic brain injury case study hesi delves into the complexities of TBI management, providing healthcare professionals with invaluable insights into diagnosis, treatment, and nursing interventions. This case study unveils the challenges and complexities of TBI, highlighting the crucial role of interdisciplinary care and patient support.
The case study presents a comprehensive overview of a patient’s journey, encompassing medical history, diagnostic procedures, treatment plan, and prognosis. It explores the intricate interplay between medical interventions and nursing care, emphasizing the significance of patient education and support.
Introduction
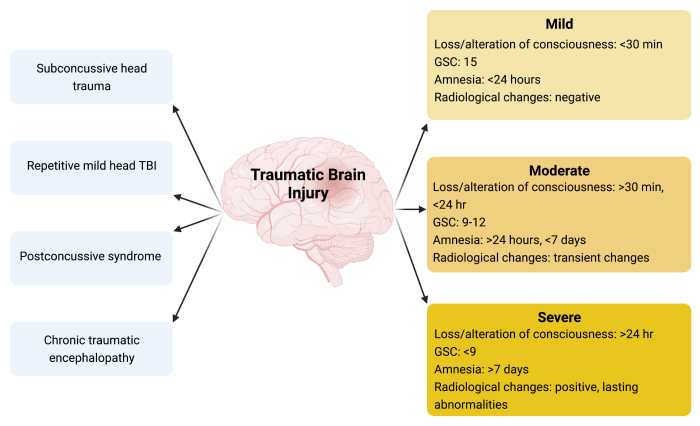
Traumatic brain injury (TBI) is a major public health concern, affecting millions of people worldwide. TBI can result from a variety of causes, including motor vehicle accidents, falls, and sports injuries. The severity of a TBI can range from mild to severe, and the symptoms can vary depending on the location and extent of the injury.
The purpose of this case study is to present the management of a patient with a TBI. The case study will discuss the patient’s demographics, medical history, presenting symptoms, diagnostic tests and procedures, diagnosis, prognosis, treatment plan, and response to treatment.
Case Study
Patient Demographics
The patient is a 25-year-old male who presents to the emergency department after being involved in a motor vehicle accident. The patient was the driver of the vehicle and was not wearing a seatbelt. The patient was ejected from the vehicle and landed on his head.
Medical History, Traumatic brain injury case study hesi
The patient has no significant past medical history.
Presenting Symptoms
The patient is awake and alert on arrival to the emergency department. He is complaining of headache, nausea, and vomiting. He also has a laceration on his forehead and a bruise on his left temple.
Diagnostic Tests and Procedures
The patient undergoes a head CT scan, which shows a small subdural hematoma in the right frontal lobe. The patient also undergoes a lumbar puncture, which shows no evidence of infection.
Diagnosis
The patient is diagnosed with a mild TBI.
Prognosis
The patient’s prognosis is good. He is expected to make a full recovery.
Treatment Plan
Medications
The patient is given acetaminophen for pain and ondansetron for nausea.
Therapies
The patient is started on physical therapy and occupational therapy.
Rehabilitation
The patient is discharged from the hospital after 2 days. He is instructed to follow up with his primary care physician in 1 week.
Discussion
Challenges in Managing TBI
There are a number of challenges in managing TBI. These challenges include:
- Diagnosing TBI
- Determining the severity of TBI
- Managing the symptoms of TBI
- Preventing complications from TBI
Potential Complications Associated with TBI
There are a number of potential complications associated with TBI. These complications include:
- Seizures
- Infection
- Hydrocephalus
- Death
Role of Interdisciplinary Care in TBI Management
Interdisciplinary care is essential for the management of TBI. A team of healthcare professionals, including physicians, nurses, therapists, and social workers, work together to provide comprehensive care for patients with TBI.
Nursing Implications: Traumatic Brain Injury Case Study Hesi
Role of Nurses in Caring for Patients with TBI
Nurses play a vital role in the care of patients with TBI. Nurses are responsible for:
- Assessing the patient’s symptoms
- Monitoring the patient’s vital signs
- Administering medications
- Providing wound care
- Educating the patient and family about TBI
Specific Nursing Interventions Required for TBI Patients
Nurses must be aware of the specific nursing interventions required for TBI patients. These interventions include:
- Maintaining a quiet and calm environment
- Limiting the patient’s exposure to stimuli
- Providing emotional support to the patient and family
- Encouraging the patient to participate in rehabilitation
Importance of Patient Education and Support
Patient education and support is essential for the management of TBI. Nurses must educate patients and families about TBI, including the symptoms, treatment, and prognosis. Nurses must also provide emotional support to patients and families.
Clarifying Questions
What are the key challenges in managing TBI?
Managing TBI poses several challenges, including the heterogeneity of injuries, limited treatment options, and the potential for long-term complications.
What is the role of nurses in caring for patients with TBI?
Nurses play a vital role in TBI care, providing comprehensive monitoring, administering medications, implementing rehabilitation interventions, and offering emotional support to patients and families.
Why is patient education and support important in TBI management?
Patient education and support empower individuals with TBI to actively participate in their recovery process, enhance their understanding of the condition, and promote self-management.