Blueprint Reading for Welders 9th Edition Answer Key is an invaluable resource for welders seeking to master the art of blueprint interpretation. This guide provides a comprehensive overview of blueprint basics, welding symbols, blueprint interpretation, dimensioning and tolerancing, welding techniques, materials and equipment, safety considerations, and real-world case studies.
By equipping welders with the knowledge and skills necessary to effectively read and interpret blueprints, this guide empowers them to produce high-quality welds that meet industry standards and specifications. Its clear and concise explanations, organized structure, and practical examples make it an essential tool for any welder seeking to advance their skills and knowledge.
Blueprint Reading Basics: Blueprint Reading For Welders 9th Edition Answer Key
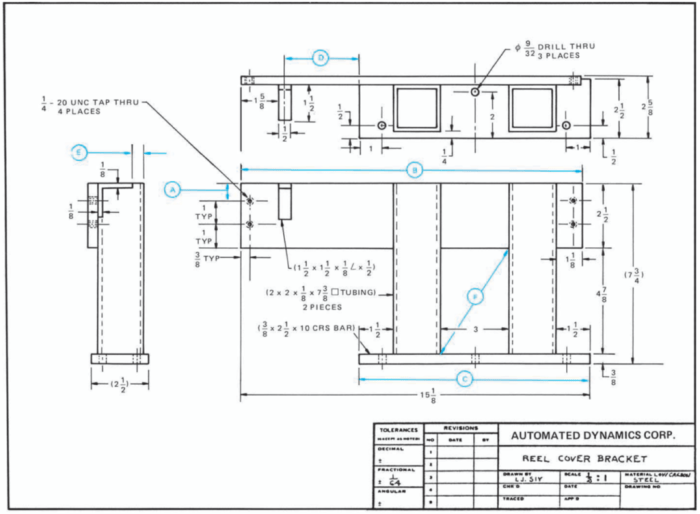
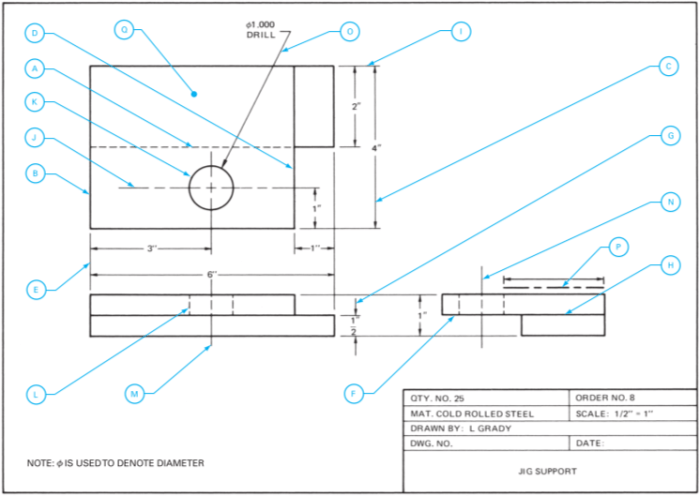
Blueprints are essential technical documents in welding, providing detailed instructions and specifications for fabricating and assembling metal structures. Understanding blueprints accurately is crucial for welders to ensure precision, safety, and efficiency in their work.
There are different types of blueprints used in welding, including fabrication drawings, assembly drawings, and welding procedure specifications. Each type serves a specific purpose, such as providing information on component dimensions, assembly sequences, and welding techniques.
Interpreting blueprints requires a systematic approach. Welders should start by identifying the title block, which contains project information such as the project name, drawing number, and revision history. They should then proceed to examine the different sections of the blueprint, including the notes, dimensions, symbols, and welding specifications.
Welding Symbols
Welding symbols are a universal language used in blueprints to convey specific welding instructions. These symbols indicate the type of weld, its dimensions, and the welding process to be used.
The American Welding Society (AWS) has standardized welding symbols to ensure consistency and clarity in blueprint interpretation. These symbols are organized into different categories, such as groove welds, fillet welds, and stud welds.
To interpret welding symbols effectively, welders need to understand the meaning and application of each symbol. For example, a triangle symbol represents a groove weld, while a square symbol represents a fillet weld.
Blueprint Interpretation
Blueprint interpretation involves the ability to visualize the three-dimensional object represented by the two-dimensional blueprint. Welders should start by identifying the overall shape and dimensions of the structure.
Next, they should focus on the individual components and their relationship to each other. Welders should pay attention to the dimensions, tolerances, and welding symbols associated with each component.
Common challenges in blueprint interpretation include deciphering complex symbols, understanding hidden features, and interpreting dimensions and tolerances correctly. Welders can overcome these challenges by using reference materials, consulting with experienced professionals, and practicing blueprint reading exercises.
Dimensioning and Tolerancing
Dimensioning and tolerancing are essential aspects of blueprint interpretation. Dimensions specify the exact measurements of the structure and its components, while tolerances define the allowable variation from these measurements.
Welders must be able to measure and interpret dimensions and tolerances accurately. They should use appropriate measuring tools, such as rulers, calipers, and micrometers, and follow the specified units of measurement.
Adhering to specified dimensions and tolerances is crucial for ensuring the proper fit and function of the welded structure. Welders should pay close attention to these specifications and make necessary adjustments during fabrication.
Welding Techniques
Blueprints often specify the welding techniques to be used for different joints and components. Welders should be familiar with the various welding techniques and their applications.
Common welding techniques include arc welding, gas welding, and resistance welding. Each technique has its own advantages and disadvantages, and welders must select the appropriate technique based on the materials, joint design, and performance requirements.
The selection criteria for choosing the appropriate welding technique include the thickness of the material, the type of joint, the desired strength and quality of the weld, and the availability of equipment.
Materials and Equipment
Blueprints specify the materials and equipment required for welding projects. Welders should carefully review these specifications and ensure they have the necessary materials and equipment before starting work.
The materials used in welding include metals, such as steel, aluminum, and stainless steel, as well as fluxes, shielding gases, and filler metals.
The equipment used in welding includes welding machines, welding torches, welding rods, and safety gear. Welders should select the appropriate equipment based on the welding technique and the materials being used.
Safety Considerations, Blueprint reading for welders 9th edition answer key
Blueprints often include safety precautions that welders must follow to minimize risks and ensure a safe work environment.
These precautions may include wearing appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE), such as welding helmets, gloves, and flame-resistant clothing. Welders should also be aware of potential hazards, such as electrical shock, arc flash, and fumes.
Following safety protocols is essential for protecting welders from injuries and health hazards. Welders should always prioritize safety and take necessary precautions when working with welding equipment and materials.
Case Studies
Case studies provide real-world examples of how blueprint reading skills are applied in welding projects.
These case studies can showcase the challenges and successes encountered during blueprint interpretation and welding fabrication.
By analyzing blueprints and discussing the techniques used to overcome challenges, case studies can enhance welders’ understanding of blueprint reading and its practical applications.
Questions and Answers
What are the different types of blueprints used in welding?
There are three main types of blueprints used in welding: fabrication drawings, assembly drawings, and detail drawings.
What is the purpose of welding symbols?
Welding symbols are used to convey specific welding instructions on blueprints. They provide information about the type of weld, the size of the weld, and the location of the weld.
What is the importance of dimensioning and tolerancing in blueprints?
Dimensioning and tolerancing provide precise measurements and acceptable variations for the components being welded. This information ensures that the welded components fit together correctly and meet the required specifications.