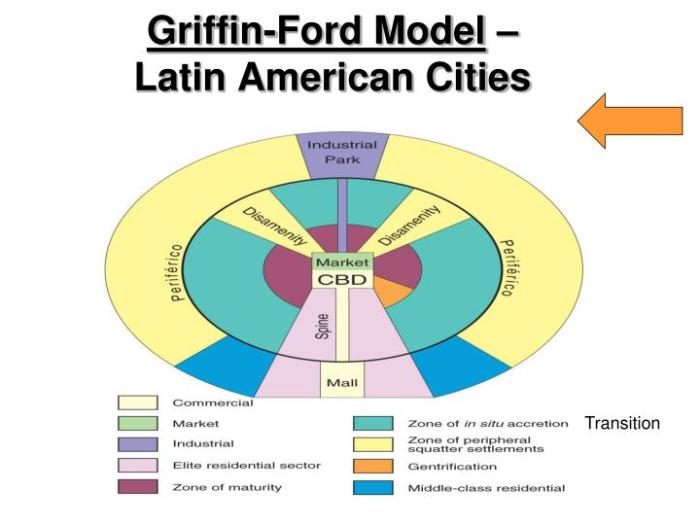
Disamenity sector ap human geography – Disamenity sectors in human geography, encompassing industries and activities that generate negative externalities, present complex challenges for communities and policymakers. This article explores the concept, types, location, and impacts of disamenity sectors, as well as strategies for mitigating their effects and promoting sustainable development.
1. Disamenity Sector in Human Geography: Disamenity Sector Ap Human Geography
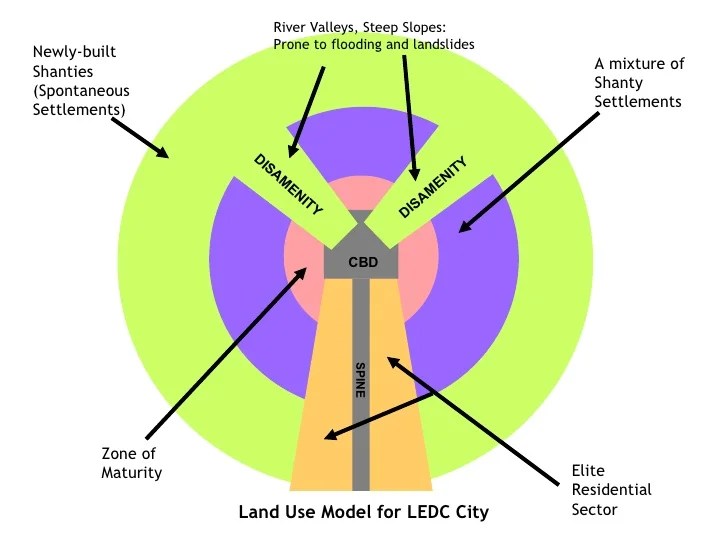
A disamenity sector encompasses industries or activities that generate negative externalities, adversely affecting the surrounding environment and communities. These sectors can include waste disposal facilities, power plants, industrial zones, and transportation infrastructure.
Disamenity sectors can significantly impact the quality of life for residents, leading to reduced property values, increased health risks, and diminished social well-being.
2. Types of Disamenities, Disamenity sector ap human geography
Disamenities can manifest in various forms, including:
- Noise pollution:Excessive noise from industrial machinery, traffic, or construction activities can disrupt sleep, impair cognitive function, and increase stress levels.
- Air pollution:Emissions from factories, power plants, and vehicles release harmful pollutants into the air, posing respiratory and cardiovascular health risks.
- Visual blight:Unsightly structures, such as landfills, scrapyards, or abandoned buildings, can detract from the aesthetic appeal of an area and lower property values.
- Traffic congestion:Heavy traffic flow associated with industrial or commercial activities can lead to delays, increased air pollution, and reduced accessibility.
- Odor pollution:Offensive smells from industrial processes or waste disposal sites can permeate the air, causing discomfort and health issues.
3. Location and Distribution of Disamenity Sectors
The location and distribution of disamenity sectors are influenced by several factors:
- Zoning regulations:Local governments use zoning laws to designate areas for specific land uses, including industrial zones that accommodate disamenity sectors.
- Land use planning:Comprehensive land use plans aim to balance economic development with environmental protection and community well-being, considering the placement of disamenity sectors.
- Economic factors:Industries seeking to minimize operating costs may locate in areas with lower land values and less stringent environmental regulations, often leading to the concentration of disamenity sectors in marginalized communities.
| Type of Disamenity | Distribution Pattern |
|---|---|
| Industrial zones | Clustered in designated areas on the outskirts of cities or near transportation hubs. |
| Waste disposal facilities | Often located in remote areas due to odor and visual blight concerns. |
| Power plants | Sited near water bodies for cooling purposes and often in industrial areas. |
| Transportation infrastructure | Roads, railways, and airports can create noise and air pollution, affecting areas along their routes. |
4. Impacts on Property Values and Land Use
The presence of disamenity sectors can significantly impact property values and land use patterns:
- Property values:Studies have shown that proximity to disamenity sectors can lead to lower property values, as potential buyers are deterred by the negative externalities.
- Land use patterns:Disamenity sectors can create barriers to development, affecting the surrounding land use mix and discouraging residential or commercial uses.
These impacts can have implications for urban planning and community development, as they influence the allocation of resources and the overall desirability of an area.
Detailed FAQs
What are the main types of disamenities?
Disamenities can include noise pollution, air pollution, visual blight, traffic congestion, and hazardous waste facilities.
How do disamenity sectors affect property values?
The presence of disamenity sectors can lower property values, as potential buyers may be deterred by the negative externalities associated with these sectors.
What role does government play in mitigating the impacts of disamenity sectors?
Government regulations, such as zoning laws and environmental standards, can help to mitigate the negative impacts of disamenity sectors by limiting their location and operation.