Introducing the Signal Transduction Pathways Answer Key, a comprehensive guide to understanding the intricate mechanisms by which cells receive, interpret, and respond to extracellular signals. This key provides a detailed overview of the components, regulation, and applications of these pathways, unlocking the secrets of cellular communication.
Signal transduction pathways are essential for a wide range of cellular processes, from growth and differentiation to metabolism and apoptosis. By elucidating the principles governing these pathways, we gain insights into the fundamental workings of life itself.
Definition of Signal Transduction Pathways
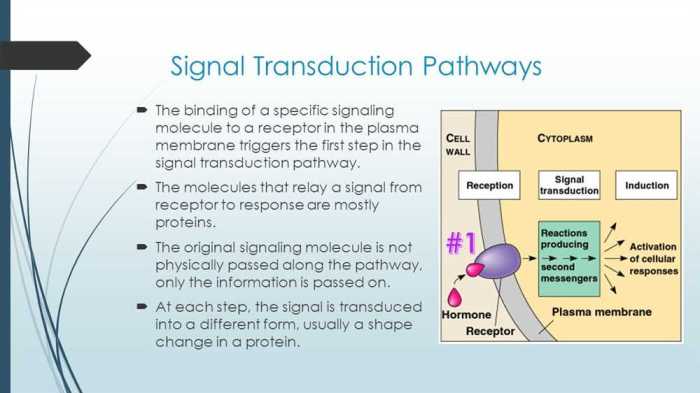
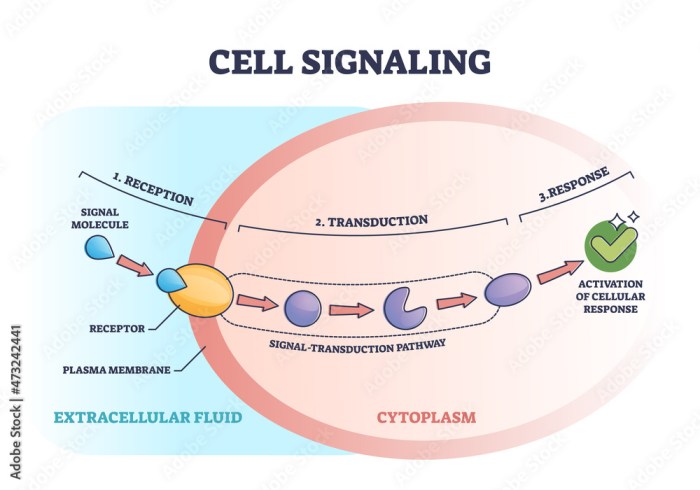
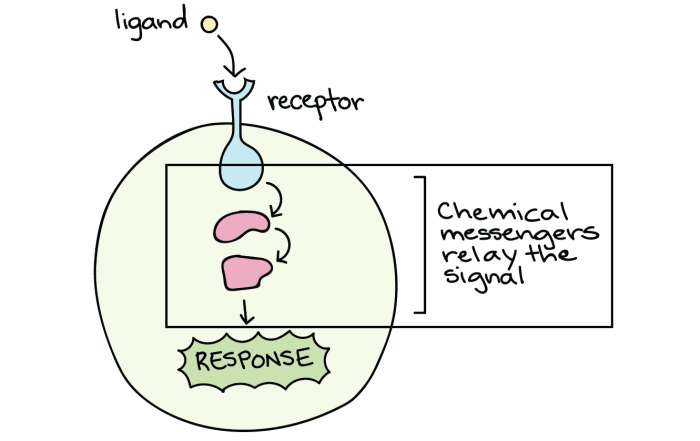
Signal transduction pathways are complex networks of molecular interactions that transmit signals from the extracellular environment to the interior of the cell. They enable cells to respond to external stimuli and regulate various cellular processes, such as growth, differentiation, and metabolism.
Receptors, located on the cell surface or within the cell, are crucial components of signal transduction pathways. They bind to specific ligands, which are signaling molecules, and initiate the transduction process.
There are several types of signal transduction pathways, including:
- G protein-coupled receptor (GPCR) pathways
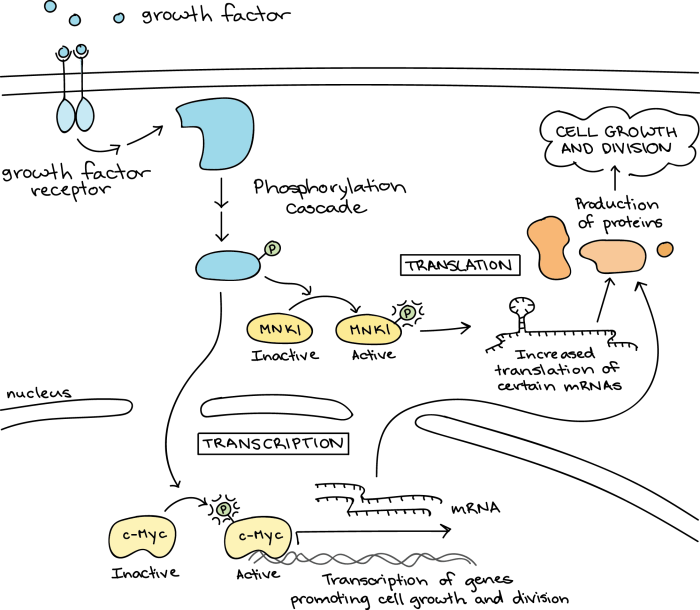
- Receptor tyrosine kinase (RTK) pathways
- Janus kinase/signal transducer and activator of transcription (JAK/STAT) pathways
- Toll-like receptor (TLR) pathways
Q&A: Signal Transduction Pathways Answer Key
What are the key components of signal transduction pathways?
Receptors, second messengers, protein kinases, and phosphatases are the key components involved in signal transduction pathways.
How are signal transduction pathways regulated?
Feedback mechanisms, such as negative feedback loops, play a crucial role in regulating signal transduction pathways.
What are the consequences of dysregulation of signal transduction pathways?
Dysregulation of signal transduction pathways can lead to various diseases, including cancer, diabetes, and immune disorders.