Introducing the Grams to Moles Calculations Worksheet, an invaluable tool for chemistry students embarking on the journey of mastering stoichiometry. This comprehensive guide delves into the fundamental concepts of converting grams to moles, equipping learners with a solid understanding of molar mass and its pivotal role in chemical calculations.
As we delve deeper into the intricacies of grams-to-moles conversions, we will uncover practical applications and explore extensions of this concept, empowering students to navigate the complexities of chemistry with confidence.
Introduction
Converting grams to moles is a fundamental skill in chemistry, allowing us to determine the amount of a substance present in a given sample. This conversion is essential for various chemical calculations, including determining the concentration of solutions, calculating reaction stoichiometry, and predicting the mass of reactants or products.
In real-world applications, converting grams to moles plays a crucial role in industries such as pharmaceuticals, food processing, and environmental monitoring. For instance, in the pharmaceutical industry, accurate conversion is necessary to ensure the precise dosage of active ingredients in medications.
Significance of Converting Grams to Moles
- Quantitative analysis:Determining the amount of a substance present in a sample, essential for chemical analysis and research.
- Stoichiometric calculations:Balancing chemical equations and predicting the mass of reactants or products involved in a reaction.
- Solution preparation:Calculating the mass of solute required to prepare solutions of a specific concentration.
- Environmental monitoring:Determining the concentration of pollutants or contaminants in environmental samples.
Understanding Molar Mass
Molar mass, also known as molecular weight, is a crucial concept in chemistry that serves as a bridge between the macroscopic and microscopic worlds. It provides a fundamental understanding of the quantitative relationship between the mass and amount of a substance.
Molar mass is defined as the mass of one mole of a substance. The mole, abbreviated as mol, is the SI unit of amount and represents a specific quantity of entities, similar to the dozen (12) for eggs or the pair (2) for shoes.
In chemistry, the mole represents exactly 6.02214076 x 10 23entities, known as Avogadro’s number.
The molar mass of a substance is expressed in grams per mole (g/mol). It is a characteristic property of each substance and provides a direct conversion factor between the mass and the amount of that substance.
Calculating Molar Mass
The molar mass of a compound can be calculated by summing the atomic masses of all the atoms present in its chemical formula. The atomic masses are obtained from the periodic table and represent the average mass of an atom of that element, taking into account the abundance of its isotopes.
Molar mass (g/mol) = Σ (Atomic mass of each element x Number of atoms of that element)
For example, the molar mass of water (H 2O) is calculated as follows:
Molar mass (H2O) = (2 x Atomic mass of hydrogen) + (1 x Atomic mass of oxygen)
Molar mass (H 2O) = (2 x 1.008 g/mol) + (1 x 16.00 g/mol)
Molar mass (H 2O) = 18.015 g/mol
The molar mass of a compound is a powerful tool that enables chemists to perform various calculations involving the quantitative analysis of substances in chemical reactions and other processes.
Step-by-Step Conversion Method
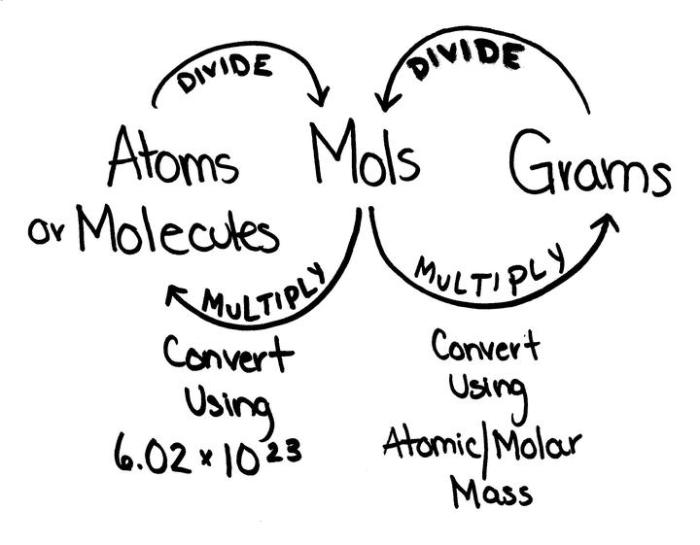
Converting grams to moles requires a straightforward, step-by-step approach. This method involves understanding molar mass and applying it to the given mass value.
The formula for converting grams to moles is:
Moles = Grams / Molar Mass
Applying the Formula
To apply the formula, follow these steps:
- Identify the molar mass of the substance. The molar mass is the mass of one mole of the substance and is typically expressed in grams per mole (g/mol).
- Divide the given mass in grams by the molar mass to obtain the number of moles.
Example:
Calculate the number of moles in 25 grams of sodium chloride (NaCl). The molar mass of NaCl is 58.44 g/mol.
Moles = Grams / Molar Mass
Moles = 25 g / 58.44 g/mol
Moles = 0.428 moles
Therefore, 25 grams of sodium chloride is equivalent to 0.428 moles.
Creating a Grams-to-Moles Worksheet: Grams To Moles Calculations Worksheet
To enhance students’ understanding of the concept of converting grams to moles, a comprehensive worksheet can be designed. This worksheet should include various elements to cater to different learning styles and provide ample practice opportunities.
The worksheet should be structured as follows:
Worksheet Structure
- Table:A table with labeled columns for grams, molar mass, and moles should be provided. This table will serve as a scaffold for students to organize their calculations.
- Practice Problems:The worksheet should include practice problems with varying levels of difficulty. These problems should range from basic conversions to more complex scenarios involving multiple steps.
- Answer Key or Solution Guide:An answer key or solution guide should be provided to allow students to check their work and identify areas for improvement.
Additional Considerations
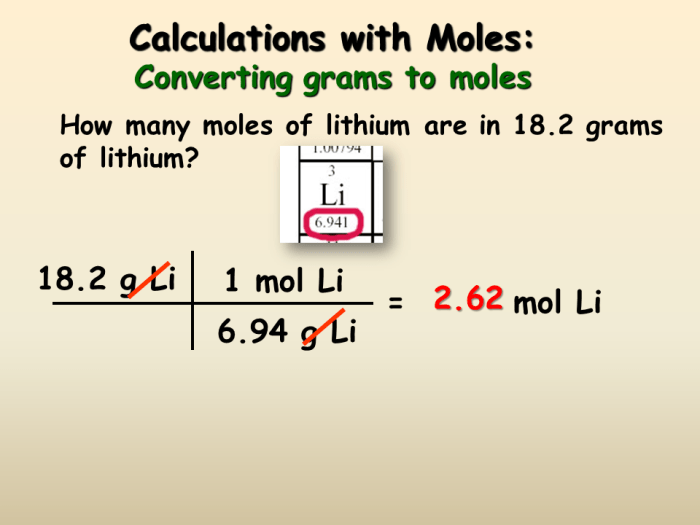
When performing grams-to-moles calculations, several factors must be taken into account to ensure accuracy and minimize potential errors.
One of the most important considerations is the accuracy of the molar mass value used in the calculation. The molar mass of a substance is a crucial factor in determining the number of moles present in a given mass of that substance.
Using Accurate Molar Mass Values, Grams to moles calculations worksheet
It is essential to obtain the molar mass value from a reliable source, such as the periodic table or a reputable chemistry reference book. Using an incorrect molar mass value can lead to significant errors in the calculation.
For example, if the molar mass of sodium chloride (NaCl) is incorrectly assumed to be 58.44 g/mol instead of the correct value of 58.44 g/mol, the calculated number of moles will be off by a factor of approximately 1.00017. This seemingly small error can have a significant impact on subsequent calculations, especially when dealing with large quantities of the substance.
Applications and Extensions
The conversion from grams to moles finds numerous applications in chemistry, aiding in various calculations and experimental procedures.
One significant application lies in determining the quantities of reactants required for a chemical reaction. By converting the given mass of a reactant to moles, chemists can ensure that the appropriate stoichiometric ratio is maintained, ensuring the successful outcome of the reaction.
Calculating Reaction Yields
Grams-to-moles conversions also play a crucial role in calculating the yield of a chemical reaction. By determining the moles of product formed and converting them to grams, chemists can quantify the amount of product obtained and assess the efficiency of the reaction.
Extending to Other Unit Conversions
The conversion method discussed in this worksheet can be extended to other unit conversions beyond grams to moles. For instance, chemists can use the same principles to convert moles to molecules, grams to atoms, or between any other units related by a known conversion factor.
Answers to Common Questions
What is the significance of converting grams to moles in chemistry?
Converting grams to moles is crucial in chemistry as it allows us to determine the number of moles of a substance present in a given mass, enabling us to perform stoichiometric calculations and predict the outcome of chemical reactions.
How does molar mass play a role in grams-to-moles conversions?
Molar mass is the mass of one mole of a substance, expressed in grams per mole. It serves as a conversion factor, allowing us to convert the mass of a substance (in grams) to the number of moles present.
What are some potential sources of error in grams-to-moles calculations?
Potential sources of error include inaccurate measurements of mass, incorrect molar mass values, and rounding errors during calculations. It is essential to use precise measuring instruments and reliable molar mass data to minimize errors.
